Tokenized GPU networks are redefining the economics and accessibility of AI compute by harnessing the principles of Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePIN). Instead of being locked behind the paywalls and gatekeeping of centralized cloud providers, high-performance GPUs can now be contributed by anyone, anywhere, to a global pool. This not only creates new income streams for hardware owners but also delivers scalable, affordable, and permissionless AI compute to developers and enterprises worldwide.

How Tokenization Unlocks Global GPU Liquidity
The core innovation is AI infrastructure tokenization. By representing physical GPUs as digital tokens on the blockchain, networks like Berkeley Compute and Aethir allow hardware owners to monetize their assets with unprecedented flexibility. Token holders gain verifiable ownership or rights to a share of compute power and its associated revenue. For example, Aethir’s pilot on BNB Chain lets investors buy into tokenized GPUs backed by future rewards from AI and gaming workloads.
This model sidesteps the inefficiencies of traditional rental markets. Instead of negotiating with opaque intermediaries or being limited by regional supply constraints, DePIN AI compute protocols aggregate idle hardware globally, creating an open marketplace where supply meets demand in real time. The result: decentralized GPU rental at price points impossible for legacy providers to match.
The Leading Tokenized GPU Networks in 2025
A wave of projects is pushing this paradigm forward. Each brings unique architecture choices but shares the mission to decentralize access to compute:
Top Tokenized GPU Networks in AI DePIN
-
Berkeley Compute: Launched in 2025, Berkeley Compute enables GPU owners to monetize their hardware by creating digital twins of physical GPUs on a decentralized platform. This system leverages blockchain for transparent ownership and revenue sharing, providing AI developers with cost-effective, tokenized compute resources.
-

Aethir: Aethir operates a global decentralized GPU cloud, pooling high-performance resources for AI and gaming. Their partnership with GAIB introduced a GPU tokenization pilot on BNB Chain, letting investors own tokenized GPUs backed by future revenue and rewards, while reducing compute costs for users.
-

Nosana: Built on Solana, Nosana offers a decentralized GPU compute grid where users contribute idle resources and earn $NOS tokens. The platform delivers affordable, efficient GPU power for complex AI workloads, bypassing the overhead of traditional cloud providers.
-

io.net: io.net aggregates idle GPUs from diverse sources, enabling rapid deployment of scalable GPU clusters for AI and machine learning. Utilizing the $IO token on Solana, it incentivizes participation and offers compute at significantly lower costs than centralized cloud services.
Berkeley Compute leads with a platform that lets users create digital twins of their GPUs for monetization and transparent revenue tracking. Aethir, meanwhile, specializes in pooling high-performance resources for both AI inference and gaming applications at scale. Their collaboration with GAIB demonstrates how tokenization can unlock new funding models for large-scale infrastructure deployment.
Nosana, built on Solana, focuses on providing affordable GPU power for complex AI workloads while rewarding contributors in $NOS tokens. io.net aggregates idle resources from diverse sources, ranging from individual miners to enterprise clusters, using $IO tokens as payment rails. This enables rapid deployment of custom GPU clusters at up to 70% lower cost than AWS or traditional clouds.
The Economic Flywheel: Incentives Drive Participation
The sustainability of these networks relies on carefully engineered incentives. Token rewards provide immediate economic motivation for contributors while simultaneously securing the network against malicious actors and downtime risk. As more users onboard, both supplying hardware and consuming compute, the value proposition compounds:
- Broad Market Access: Startups and researchers bypass capital barriers by renting decentralized GPUs instead of investing in expensive hardware upfront.
- Diversified Revenue Streams: Hardware owners earn passive income from otherwise idle assets via transparent blockchain payments.
- Ecosystem Resilience: The distributed nature reduces single points of failure, improving uptime and reliability compared to centralized alternatives.
This dynamic has catalyzed a surge in participation across both sides of the market, from solo miners seeking yield diversification to deep tech labs needing scalable inference capacity at predictable costs.
As these decentralized GPU networks mature, their ability to scale flexibly and price competitively is setting a new standard for AI compute provisioning. Tokenized GPU networks are not just lowering the barrier to entry; they are also fostering a global marketplace where innovation is no longer stifled by geographic or capital constraints. The result is a more inclusive ecosystem where developers from emerging markets can access the same high-performance compute as large enterprises, leveling the AI playing field in unprecedented ways.
Regulatory clarity and robust network governance remain essential. Projects like Nosana and io. net are actively developing on-chain reputation systems and staking mechanisms to ensure quality of service, mitigate bad actors, and build trust among participants. These frameworks allow contributors to be rewarded not just for raw compute supplied, but also for reliability and uptime, aligning network health with individual incentives.
Challenges Ahead: Network Effects and Interoperability
The path forward is not without hurdles. Achieving seamless interoperability between different DePIN AI compute protocols will be crucial for sustained growth. Fragmentation could dilute liquidity and reduce efficiency; thus, cross-chain bridges, open APIs, and shared standards will play pivotal roles in uniting disparate networks into a cohesive global resource layer.
Another challenge lies in onboarding traditional enterprises. While cost savings are compelling, often up to 70% lower than centralized clouds, risk-averse organizations require robust SLAs, auditability, and compliance assurances before migrating critical workloads. The most successful networks will be those that can abstract away blockchain complexity while delivering enterprise-grade reliability at scale.
Key Challenges for Tokenized GPU Networks in 2025
-

Resource Verification & Trust: Ensuring the authenticity and reliability of contributed GPU resources remains a primary challenge. Berkeley Compute and Aethir are developing on-chain attestation and real-time monitoring systems to validate GPU performance and prevent fraudulent resource claims.
-

Network Latency & Geographic Distribution: Decentralized networks face latency and data transfer bottlenecks due to the global dispersion of nodes. io.net and Nosana are implementing intelligent workload routing and edge computing strategies to optimize task allocation and minimize latency.
-
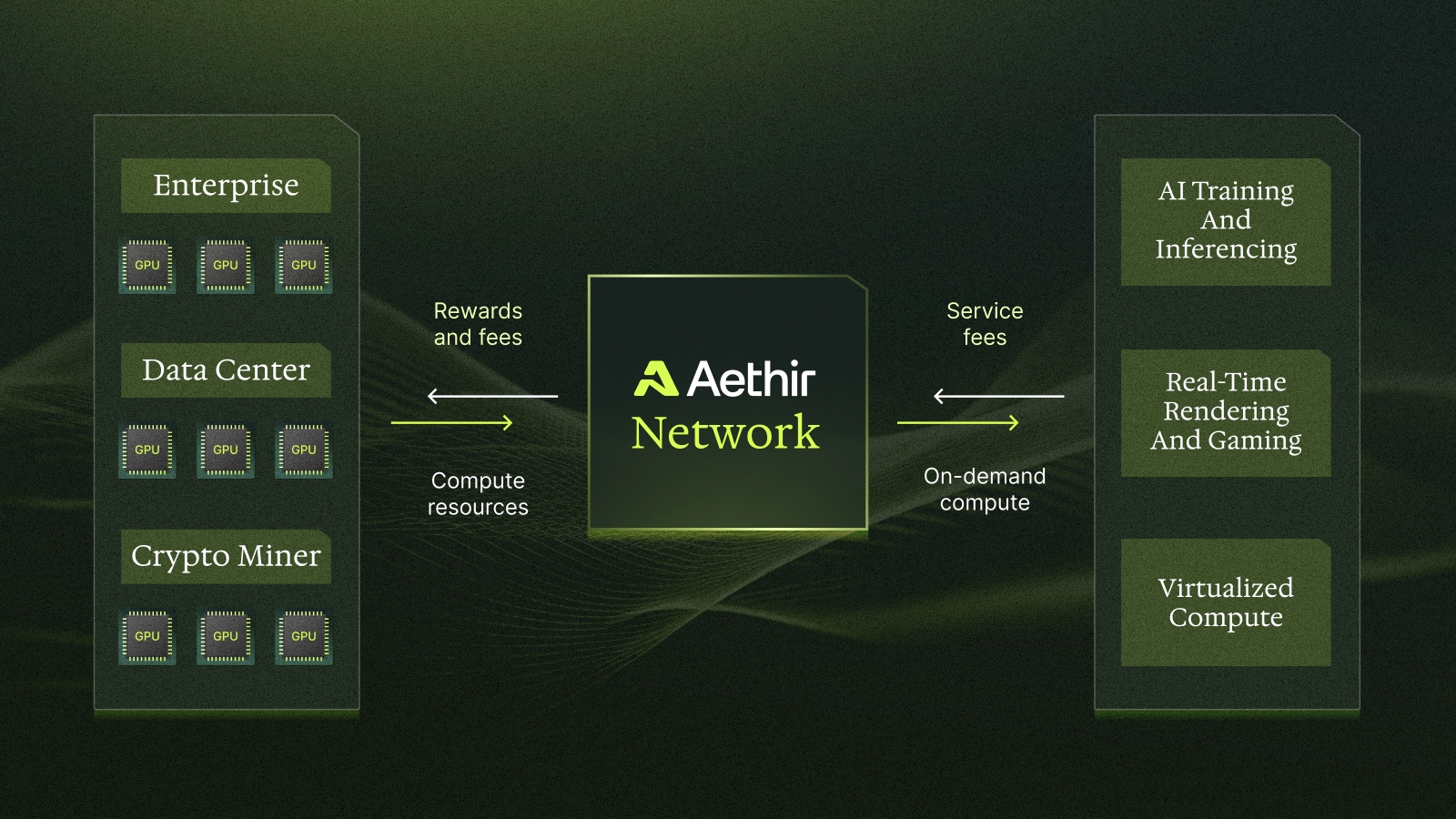
Incentive Alignment & Tokenomics: Maintaining a sustainable incentive structure for both GPU providers and users is complex. Projects like Nosana and Aethir are refining dynamic pricing models and staking mechanisms to balance supply, demand, and long-term network health.
-
Interoperability & Standardization: Integrating diverse GPU hardware and software stacks is a technical hurdle. Berkeley Compute and io.net are advancing cross-platform compatibility layers and unified APIs to streamline onboarding and broaden network participation.
-

Regulatory Compliance & Data Privacy: Operating across jurisdictions introduces regulatory and privacy risks, especially for sensitive AI workloads. Leading networks are exploring privacy-preserving computation and compliance frameworks to meet evolving legal requirements.
The Roadmap for Decentralized AI Compute
The momentum behind crypto-powered AI compute shows no sign of slowing. As tokenized GPU networks continue to attract both supply- and demand-side participants, network effects are expected to drive exponential growth in available resources and supported workloads. This virtuous cycle will further compress costs while expanding access, a flywheel effect that benefits all stakeholders.
For innovators building on top of these platforms, the future holds immense promise: permissionless scaling for generative models, privacy-preserving federated learning across borders, and even new business models where end-users directly participate in AI value creation. The convergence of DePIN architecture with advances in zero-knowledge proofs and secure enclaves may unlock even more sophisticated use cases around data sovereignty and confidential computing.
The coming years will see fierce competition among projects vying to become the default infrastructure layer for decentralized AI workloads. Those who can balance cost efficiency with reliability, and incentivize sustained participation at every layer, will shape the next era of global computation.






